The research team from the Computational and Exploration Geophysics Research Center at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology (APM) has achieved new progress in the high-precision suppression of multi-source noise in Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) Vertical Seismic Profiling (VSP) data. Addressing the issue of DAS-VSP data being contaminated by a large amount of random noise and coherent coupled noise, the research team designed an exponential decay curve-constrained empirical mode decomposition (EDCC-EMD) frequency-domain supervised denoising network model. This method significantly improved the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of DAS-VSP data, successfully recovered weak signals masked at deep levels, overcame inversion challenges caused by low-SNR data, and provided reliable technical support for high-precision underground structure imaging. Recently, the relevant research findings have been published in "Petroleum Science" and featured as a highlighted paper.
DAS technology has developed rapidly in recent years and has become an important breakthrough in the field of seismic exploration, especially showing broad prospects in VSP applications. However, actually collected DAS-VSP data is often severely interfered with by strong coherent coupled noise and random noise, significantly affecting data quality and the accuracy of subsurface imaging. Most existing deep learning-based denoising methods rely on noise labels generated by traditional denoising techniques, making it difficult to accurately adapt to the unique noise characteristics of DAS data and limiting their application effectiveness in oil and gas exploration.
To address this challenge, the research team innovatively proposed a supervised denoising network based on an exponential decay curve-constrained empirical mode decomposition (EDCC-EMD). This method first uses traditional EMD to extract initial noise components from field DAS-VSP data and then performs a secondary EMD decomposition on these components to obtain a series of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs). By analyzing the correlation coefficients between each IMF and the initial noise and introducing an Exponential Decay Curve (EDC) as a constraint, purer noise components are extracted. The optimized noise labels significantly enhance the training quality and generalization performance of the denoising network.
It is worth noting that existing methods mostly focus on time-domain feature analysis, often neglecting key distinguishing features contained in frequency-domain information. This study innovatively uses frequency-domain data as input for network training, fully leveraging the more pronounced separability between noise and signals in the frequency domain, greatly improving the network's learning efficiency and denoising performance in noise-signal separation tasks, and providing a new technical pathway for high-precision processing of DAS-VSP data.
The research results indicate that the method proposed by the research team demonstrates superior denoising performance. In tests on filed deep weak-signal DAS-VSP data, this method significantly improved the SNR by up to 22.9 dB, outperforming traditional denoising methods (such as EMD and FK) as well as the classic time-domain U-net noise suppression method. This method performs better in both noise suppression and signal fidelity preservation, and it can effectively correct phase distortions caused by noise contamination, fully proving its advanced nature and practical value in DAS-VSP data processing.
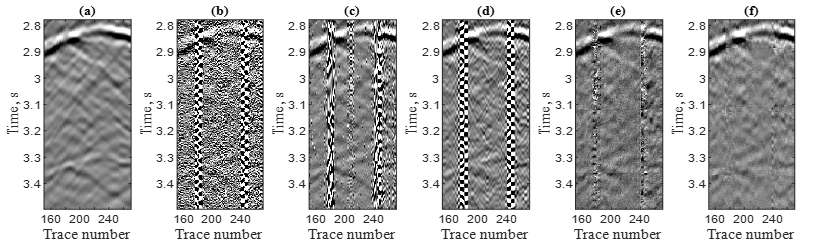
Denoising results for deep weak-signal DAS-VSP data. (a) Clean data; (b) Noisy data (-17.6 dB); (c) Denoising result using the EMD method (0.2 dB); (d) Denoising result using the FK method (0.1 dB); (e) Denoising result of our method in the time domain (2.1 dB); (f) Denoising result of our method in the frequency domain (5.3 dB), with an SNR increase of 22.9 dB.
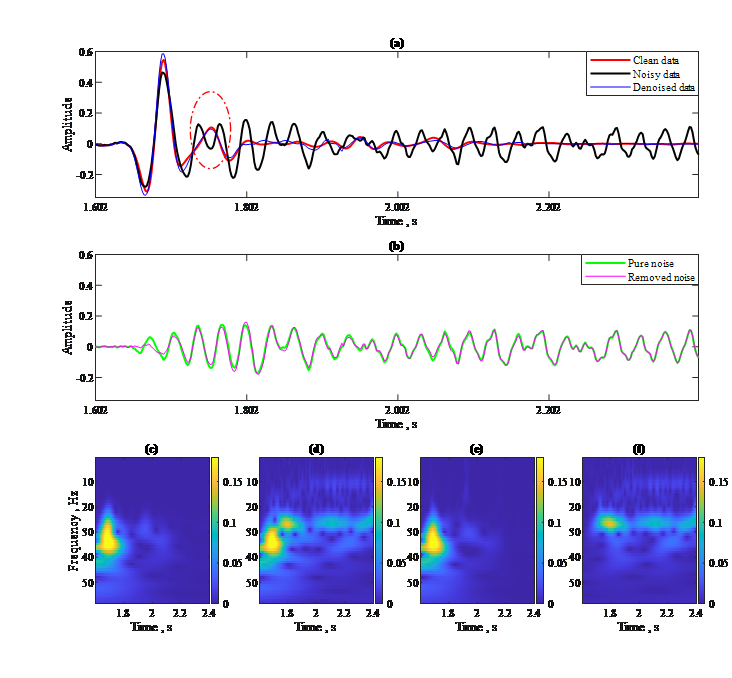
Amplitude and phase details of DAS-VSP data after denoising by our method. (a) Waveform of a single trace; (b) Pure noise and removed noise components. (c)-(f) Respectively show the time-frequency spectra of clean data, noisy data, denoised data, and removed noise.
This method overcomes inversion challenges caused by low-SNR data and has strong versatility, with the potential for direct application in various scenarios such as conventional geophone seismic data and seismic array data, demonstrating broad industry application prospects and providing reliable technical support for high-precision underground structure imaging.
The relevant research findings were published in Petroleum Science under the title "An EDCC-EMD analysis-based network for DAS VSP data denoising in frequency domain". APM served as the first completing institution, with young associate researcher TANG Huanhuan as the first author and researcher MAO Weijian as the co-corresponding author.
This research was supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Link to the article: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petsci.2025.03.006
